FdF
My FdF notes.
FdF
This will just be a thought collection or code snippet storage. Not a detailed walkthrough or example of FdF.
This project involves creating a simple wireframe model of a landscape.
Overview
This project is about creating a simple wireframe model representation of a 3D landscape by linking various points (x, y, z) thanks to line segments (edges).
Rendering
Your program has to represent the model in isometric projection. The coordinates of the landscape are stored in a .fdf file, provided as a command line parameter to your program. Here is an example:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
$>cat 42.fdf
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 10 10 0 0 10 10 0 0 0 10 10 10 10 10 0 0 0
0 0 10 10 0 0 10 10 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 10 10 0 0
0 0 10 10 0 0 10 10 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 10 10 0 0
0 0 10 10 10 10 10 10 0 0 0 0 10 10 10 10 0 0 0
0 0 0 10 10 10 10 10 0 0 0 10 10 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 10 10 0 0 0 10 10 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 10 10 0 0 0 10 10 10 10 10 10 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
$>
this should result in something like this: 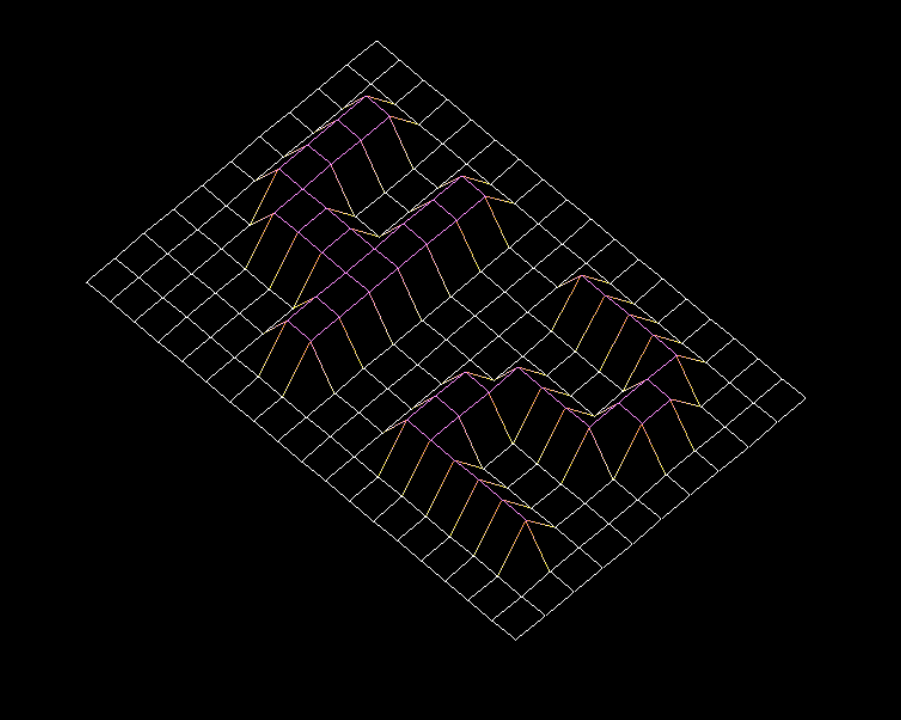
Graphic management
Your program has to display the image in a window.
- Window management must remain smooth (e.g., switching to another window, minimizing, etc.).
- Pressing ESC must close the window and quit the program in a clean way.
- Clicking on the cross on the window’s frame must close the window and quit the program in a clean way.
- The use of the images of the MiniLibX library is mandatory
Map parsing

- Read the entire map into
char *file_buffer. - Split
char *filebufferintochar **line_arrayby splitting on the\ncharacter. - Split
char **line_arrayintochar ***char_arrayby splitting on the spaces. This will create a 2d string array with a string for each map coordinate. - Create a 2d struct array
t_coord **pix_arrayaccording to the dimensions ofchar ***char_array. - fill in the height and colour in the
t_coord **pix_arrayaccording to the content ofchar ***char_array.
Math
Rotating
The following Rotation matrix is applied to the point cloud created to rotate the points around the corresponding axis. After this a translated point-map is made and passed on to draw lines in between these points.
\[{\displaystyle {\begin{alignedat}{1}R_{x}(\theta )&={\begin{bmatrix}1&0&0\\0&\cos \theta &-\sin \theta \\[3pt]0&\sin \theta &\cos \theta \\[3pt]\end{bmatrix}}\\[6pt]R_{y}(\theta )&={\begin{bmatrix}\cos \theta &0&\sin \theta \\[3pt]0&1&0\\[3pt]-\sin \theta &0&\cos \theta \\\end{bmatrix}}\\[6pt]R_{z}(\theta )&={\begin{bmatrix}\cos \theta &-\sin \theta &0\\[3pt]\sin \theta &\cos \theta &0\\[3pt]0&0&1\\\end{bmatrix}}\end{alignedat}}}\]Drawing lines
Bresenham’s line algorithm is used for the calculation do draw pixels on a line. This is a expansion on the basic y=mx+b formula.